前段时间帮一个同学做了套MySQL的笔试题目,感觉有一定难度,有一段时间没写过SQL语句了,练练手,大佬不要嘲笑嗝。

Create Table ‘Sales’
1 | CREATE TABLE `sales` ( |
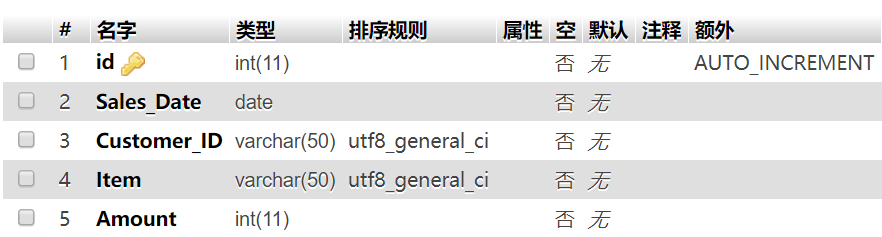
Init Data
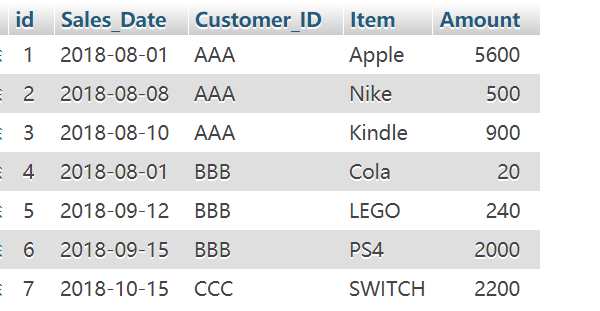
1 | INSERT INTO `sales` (`id`, `Sales_Date`, `Customer_ID`, `Item`, `Amount`) VALUES |
Query_1
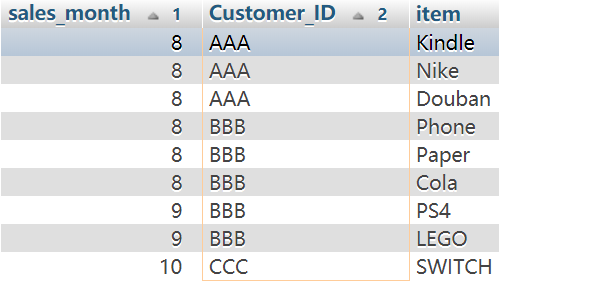
We need to calculate the amount for each user and month, so we will use group by sales_month, customer_id. And then we can add a condition to make the total_amount between 2000 and 10000. Month(Date) can calculate the month of the date.
1 | SELECT month(Sales_Date) as sales_month, Customer_ID, sum(amount) as total_amount |
Query_2
这个好难,感觉leetcode的hard难度都不止。。我可以做到这样列出来,然后
1 | SELECT month(Sales_Date) as sales_month, Customer_ID, item |
1 | SELECT month(Sales_Date) as sales_month, Customer_ID, GROUP_CONCAT(item SEPARATOR '|') as top3 |
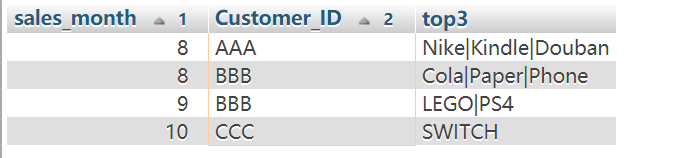
First of all, we should know how to make multiple rows to one row, we can use GROUP_CONCAT.
Then we need to process the date group by group, we use a sub query and the condition < 3 .
And I think get the order right is also important. The first is sales_month, then customer_id, and finally amount.
Query_3
1 | with t1 as ( |
Pre-query t1 and t2 query for the purchase log of July and August. And query p is calculate for the MoM_Decrease for each item, we use the FULL OUTER JOIN here. Then we can add the rank for the result.
Query_4
1 | with t as ( |
First we use pre-query to find the rows in 2018/08. After that we can use a simple query to find the customers who have purchased in at least three consecutive.
在mysql的规范中,并不包含连续性的相关方法,所以按照通常来说,我们应该使用其他方式查询该题所需的数据【例如一些脚本语言,可以使用更方便快捷的算法】。